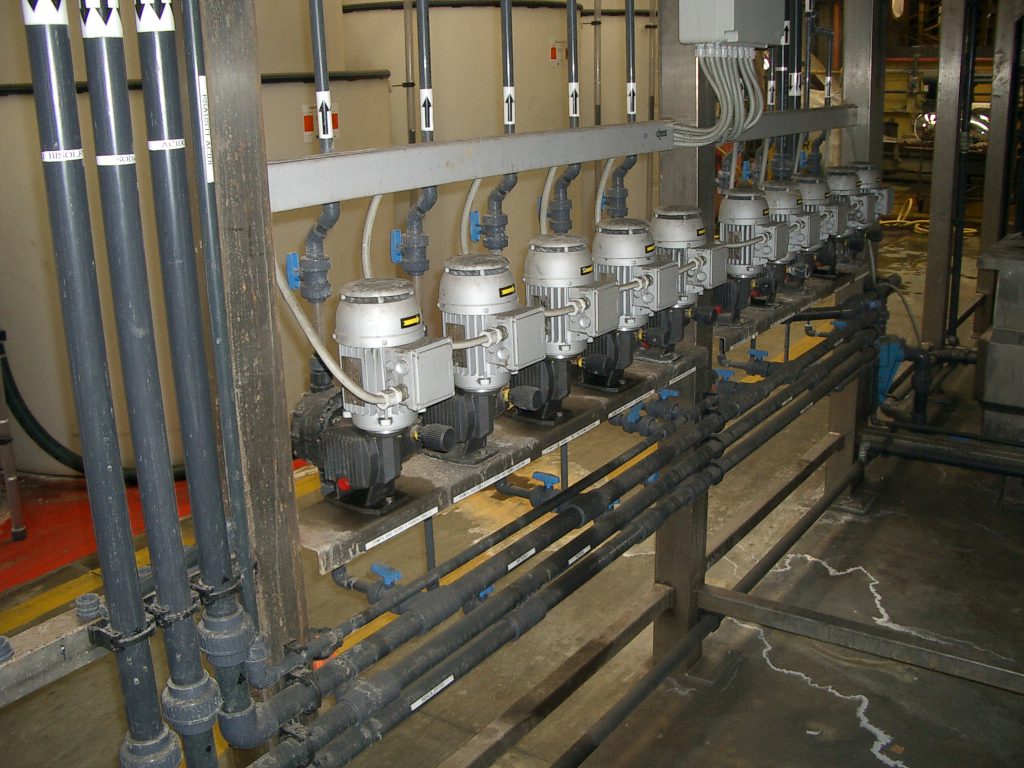
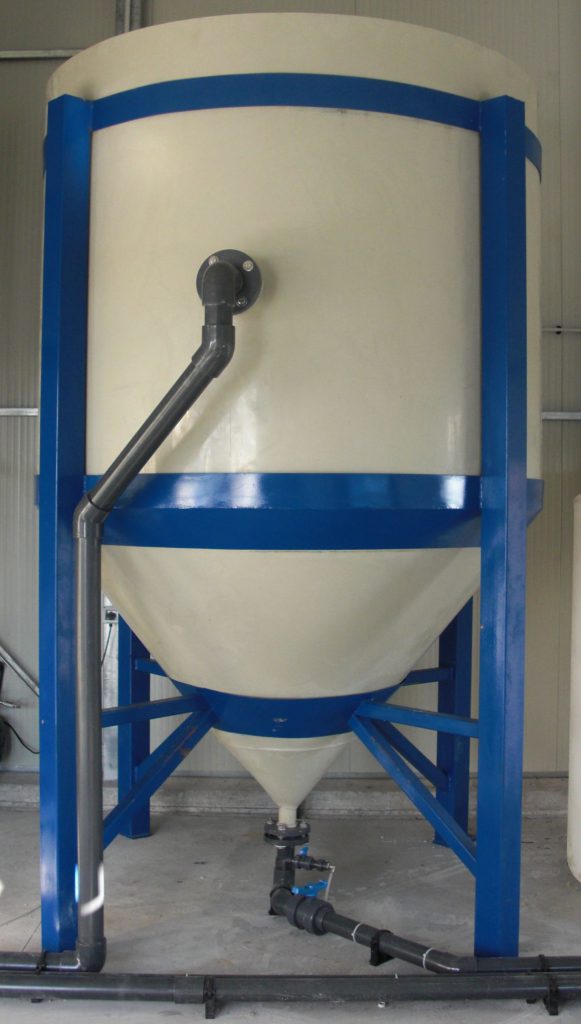
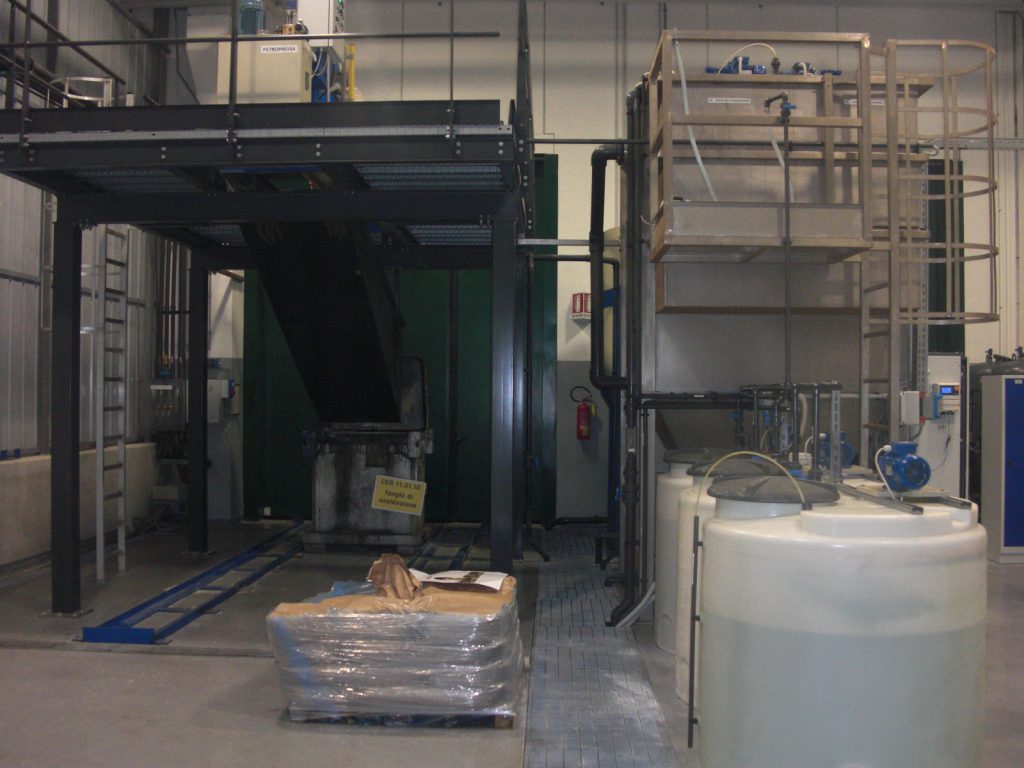
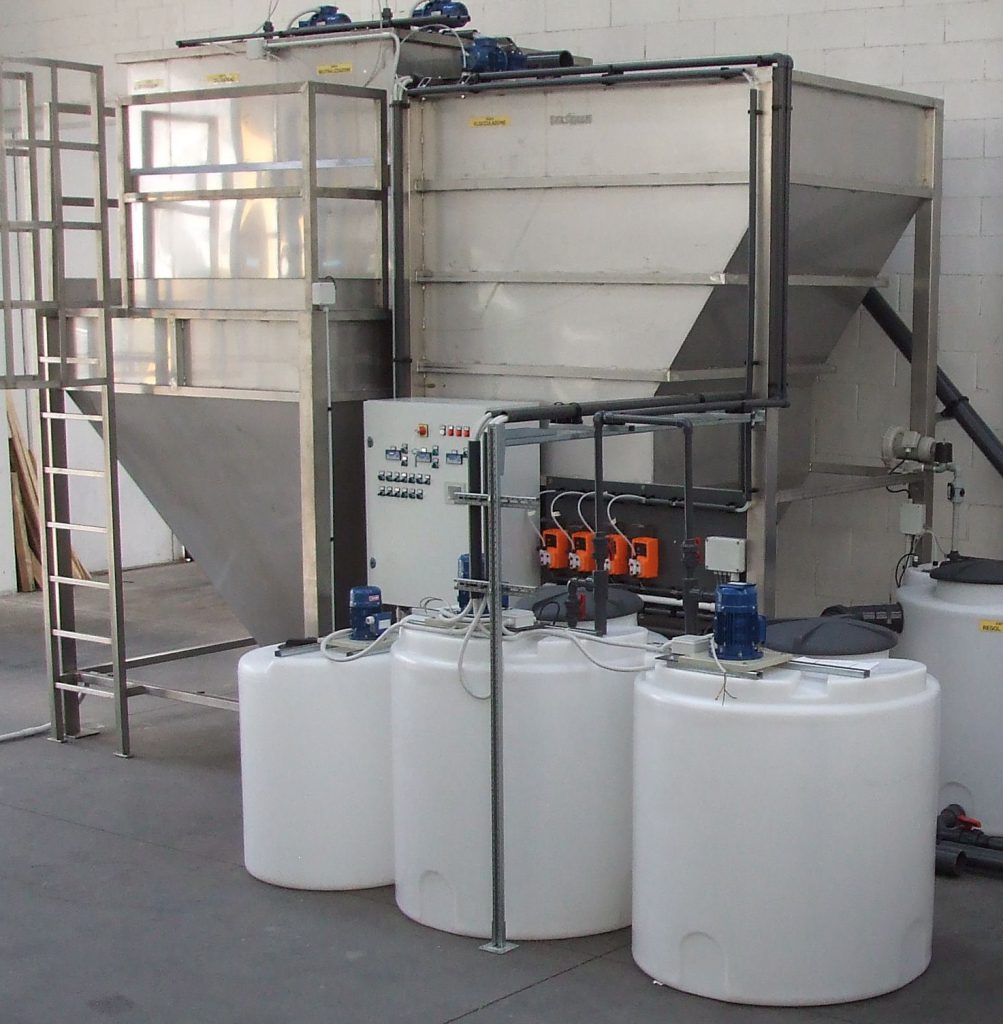
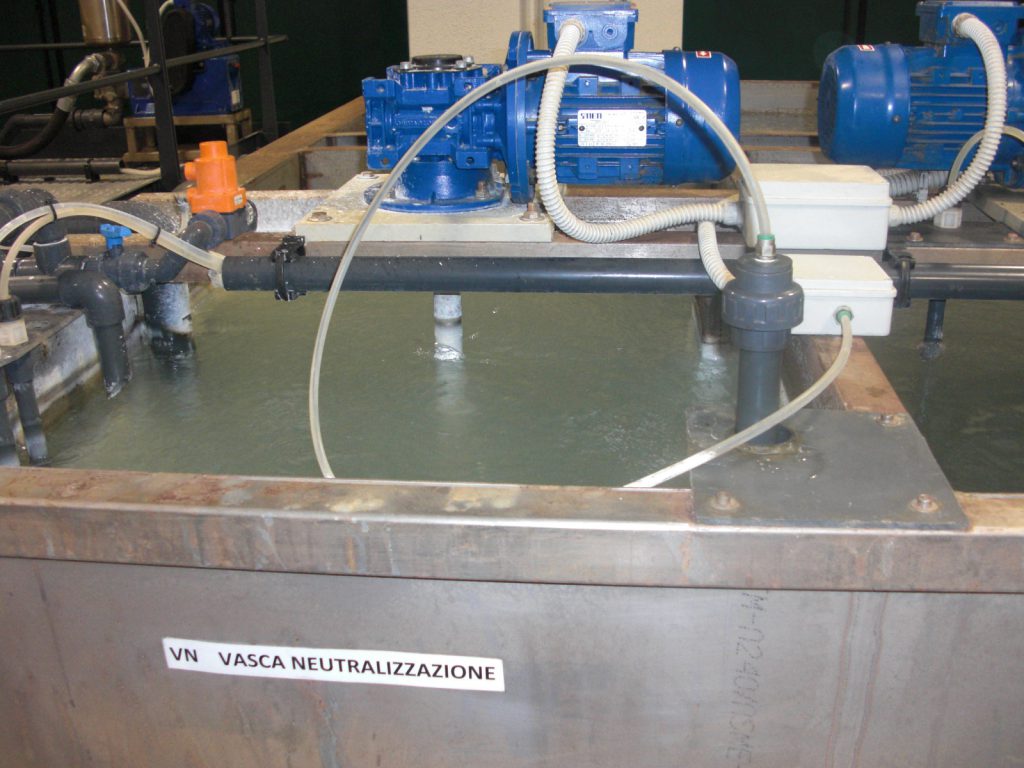
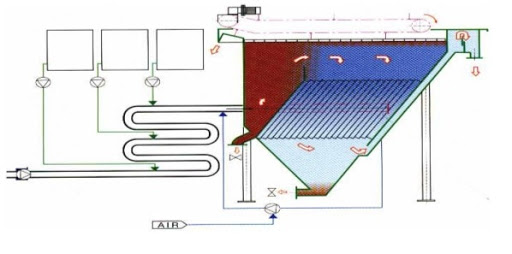
Coagulation is a section that in a physical-chemical plant is really important, the agglomeration of the particles creates the matrix for a subsequent uniform presence of sludge flakes, this reaction is created by Van der Waals type forces.
The coagulation capacity of chemicals increases thanks to the charge – ion beam ratio, for this reason it is necessary to use the correct coagulating agent in water purification plants.
Pentacque uses these primary coagulant products in the design of its chemical-physical purification plants:
Aluminum sulphate Al2 (SO4) 3
Marketed in granules and powder, it has a good coagulating action at pH 6.6 – 7.5 the flocculation and the mud hydroxide take a whitish color. As with all aluminum salts in a water treatment plant, attention must be paid to the possibility of redissolution at basic pH.
Basic aluminum chloride (polychloride aluminum) (Al (OH) Cl2) 5
Basic aluminum chloride salt marketed in liquid form, dosed in purification plants, has a higher coagulating power than aluminum sulphate in almost all cases of use, the pH of use of this coagulant is between 6.00 and 8.50.
Sodium aluminate Na2AL2O4
Sold in liquid solution dosed in a physical chemical plant, it forms flakes of aluminum hydrate that are negatively charged, this coagulant must be used in conjunction with aluminum sulfate that makes a positive charge, this mix is used in special cases and difficult to purify.
Ferric chloride FeCl3 6H2O
Normally marketed in liquid form, there is however a solid version, it is the most widely used coagulant in chemical-physical purification plants because it has a good coagulant power, superior to that of aluminum sulphate.
Its wide use in water treatment plants is also due to the higher pH range of the other coagulants, which varies from 6.00 to 10.00.
Ferrous sulphate FeSO4 7H2O
It is marketed in soluble solid form, has the same coagulating characteristics as ferric chloride, an additional technical feature much appreciated in galvanic water purification systems, is to avoid the oxidation of trivalent chromium in hexavalent. The working pH in the chemical physical purification plant is between 6.00 and 10.00.